USB4 与 Thunderbolt 4 备忘
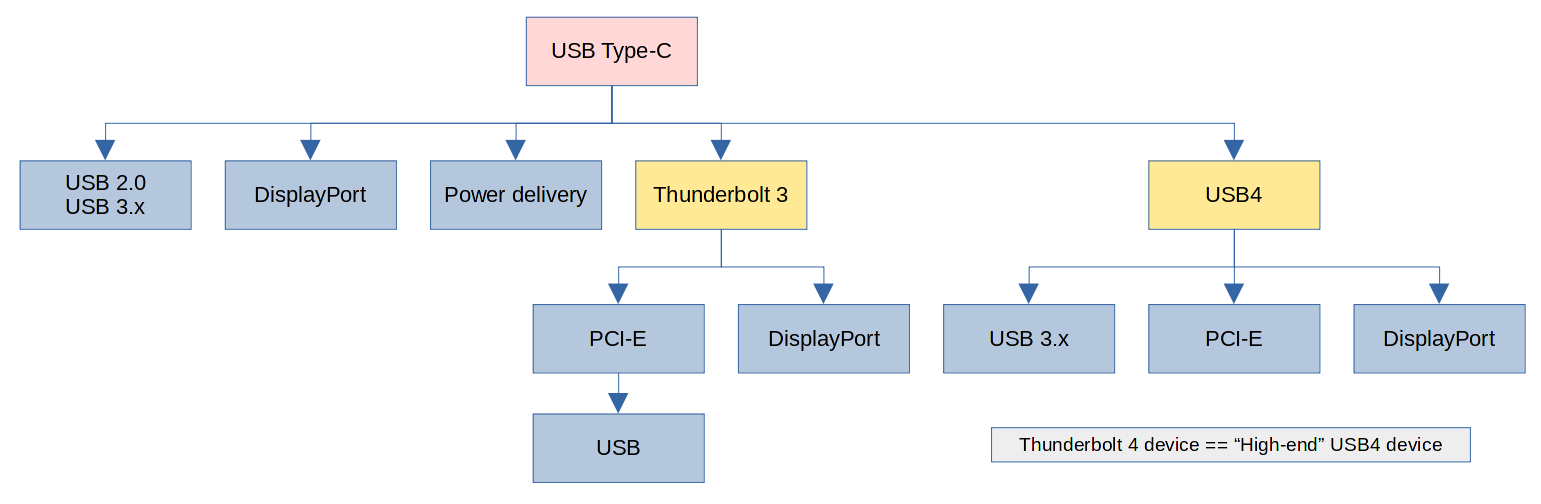
最近研究了一些关于 USB4 以及 Thunderbolt 4 的资料,在此做个备忘。目前只考虑 USB Type-C 接口,并且忽略 Type-C 可以正反随意插带来的复杂性。
- USB Type-C 接口里有一对(两根)差分信号线,用于 USB 2.0 协议(USB 2.0, 480 Mbps)。
- USB Type-C 接口里有四根 GND 以及四根 V_BUS 用于送电,具体电压和电流由两端使用 CC 线协商 (Power delivery)。
- 在 Type-C 接口里再取两对差分信号线,用于 USB 3.x 协议(USB 3.2 Gen 1, 5 Gbps)。
- 通过改进协议,可以将传输速度翻倍(USB 3.2 Gen 2, 10 Gbps)。
- 再把 Type-C 中最后剩下四根信号线也用上,传输一样的协议,可以将速度再次翻倍(USB 3.2 Gen 2x2, 20 Gbps)。
- 大家发现这八根高速信号线不止可以用于 USB,也可以用来传输其他信号。比如:电脑可以与显示器透过 CC 线协商,使用两对差分信号线传输 DisplayPort 信号(DP Alt mode)。
- Intel 觉得 Type-C 接口不错,于是有了 Thunderbolt Alt mode,使用全部四对差分信号线传输 Thunderbolt 协议(Thunderbolt 3, 40Gbps)。
Thunderbolt 3 本身是一种隧道协议,在这个隧道中可以传输 PCI-E 数据和 DisplayPort 数据。
至于 USB 则可以在扩展坞中内置一个 USB 控制器芯片,通过 PCI-E 与电脑连接,这样扩展坞就可以插 USB 设备了。 - USB-IF 觉得 Thunderbolt 3 这个协议不错,在 Intel 开放了 Thunderbolt 3 协议后,就把它拿过来“改名”成了 USB4。使用 USB Type-C 中的两对或四对差分信号线传输(USB4, ~40Gbps)。
与 Thunderbolt 3 相同,USB4 也是一种隧道协议,其中可以传输 USB 3.2,PCI-E,DisplayPort 等协议。
(吐槽时间:外层协议和内层协议都叫 USB 你是认真的吗?)
USB4 规范并不要求硬件生产厂家实现所有功能,比如说,一个最高只支持 20Gbps 速度的设备可以合法地被称作“支持 USB4”。因为 USB4 规范并不要求所有设备都支持 40Gbps。(吔屎啦你 USB-IF) - Intel 觉得 USB-IF 的标准混乱,是赚钱的好机会,于是自己列了一套更高的标准(比如要求设备必须支持 40Gbps 速度),并给符合 Intel 的标准的设备贴上 “Thunderbolt 4” 的标签。
最后围观 USB4 混乱的速度要求被鞭尸的现场:https://youtu.be/ly5-QHjs8Gw?t=1845
Allison Sheridan: So a Thunderbolt 4 device is a USB4 device...
Brad Saunders: (nodding)
Allison Sheridan: ...but a USB4 device is not necessarily a Thunderbolt 4 device?
Brad Saunders: It can be ...
Allison Sheridan: It can be but it isn't necessarily.
Brad Saunders: It'll probably have... they may have made a choice to... maybe it's only 20 Gbps.
Allison Sheridan: Right, but it's Thunderbolt 4 it's 40 [Gbps] per second, Okay.